38 label the carrier proteins in model 3
Trapping Interactions Between Catalytic Domains and Carrier Proteins of ... Very recently, the electrophilic vinylsulfonamide inhibitors have been exploited to specifically label carrier protein domains providing additional proteomic profiling tools. 70 The probes were designed to contain an alkyne on the 2'-hydroxyl of the inhibitor. As demonstrated in the prior biochemical and structural studies, the new probes ... Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain Outer | Chegg.com Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the innet mitochondrial Question: Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain Outer mitochondrial membrane H Н. H incon oxygen Mitochondrial matrix AD GUADINAD Inner mitochondrial membrane ADH FAD (H.0 14.
PDF 3 Protein Structure-S - Norwell High School With your group, write a grammatically correct sentence that summarizes how the secondary protein structure is formed from the primary structure. Protein Structure 5 Model 3 - Protein Structure (Part B) Tertiary Structure H CH 2 CH 3CH 3 CH
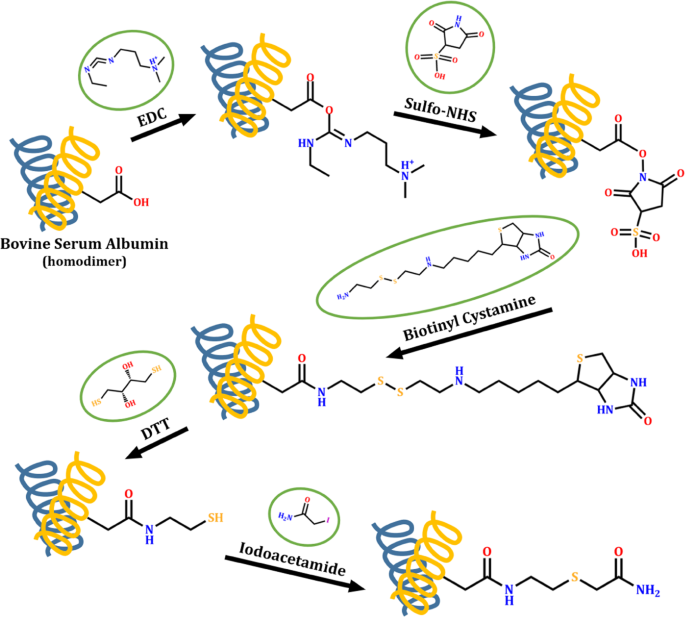
Label the carrier proteins in model 3
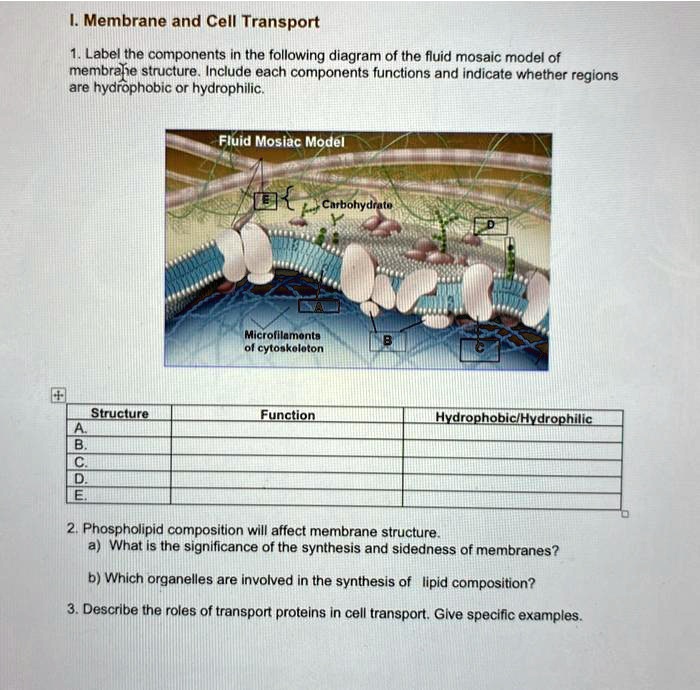
Carrier Protein - Definition, Function and Examples - Biology Dictionary Carrier Protein Definition Carrier proteins are proteins that carry substances from one side of a biological membrane to the other. Many carrier proteins are found in a cell 's membrane, though they may also be found in the membranes of internal organelles such as the mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleolus, and others. Label-free and redox proteomic analyses of the triacylglycerol ... The expression of proteins involved in the degradation of branched-chain amino acids and the methylmalonyl-CoA pathway probably provided propionyl-CoA for the biosynthesis of odd-numbered fatty acids, which make up almost 30 % of RHA1 fatty acid composition. ... [acyl-carrier protein] synthase II (FabF). An integrative metabolic model for the ... PDF Chapter 3 Review Materials Key - wtps.org 9. What name is given to the transmembrane proteins that allow this direct passage? 3. Figure 3.3 is a simplified diagram of the plasma membrane. Structure A repre- sents channel proteins constructing a pore, structure B represents an ATP- energized solute pump, and structure C is a transport protein that does not depend on energy from ATP.
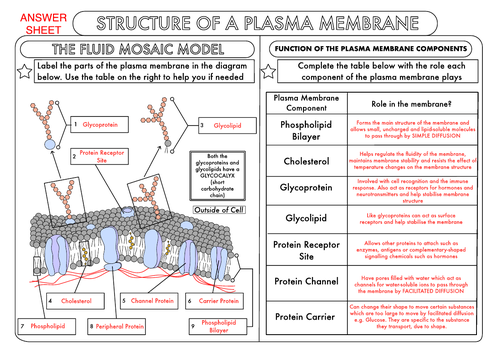
Label the carrier proteins in model 3. Week 3: Membrane Transport Flashcards | Quizlet Sort the following types of membrane transport mechanisms into active or passive processes. Active Process: Secondary active transport, Primary active transport, Endocytosis, Exocytosis. Passive Process: Simple diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, Osmosis. The cellular plasma membrane is selectively permeable, which means some materials move ... Biology Ch 4 Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Label the following image with the correct terms to describe the structure and function of a plasma membrane., The cell membrane is composed of a ____, meaning there are two layers of ____., In the outer layer of the membrane, the ____ head points outward towards the external environment. and more. Understanding the effect of carrier proteomes in single cell proteomic ... plex with isobaric labels vs. 3-plex with SILAC), and the con-cept of a carrier proteome has evolved within these new multiplexing approaches. Potentially the first instance of a carrier proteome within an isobaric label-based multiplexed proteome experiment was the TMCcalibrator approach 18(Figure 2). Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell - Chegg Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. (Which ones are the cytochromes?) 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the Question: Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell wall dectron oxygen cell membrane ADP ATP NADH NAD FADH FAD (HO) 14. What cell structure is the site for the electron transport chain?
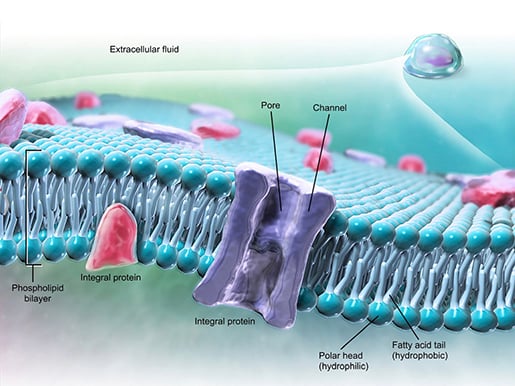
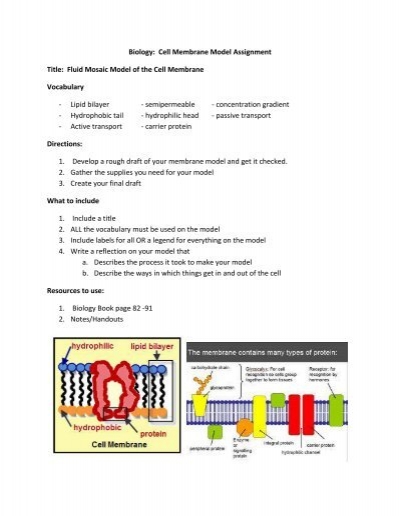
PDF Phospholipid & Membrane Transport Kit Student Handout 3 You will use a simplified representation of the phospholipid bilayer in this activity. 1. Label thehydrophilic headand hydrophobic tailin the photos below. CPK Color Scheme Oxygen (red) Nitrogen (blue) Hydrogen (white) Carbon (grey) Phosphorus (yellow) Center area is a convenient way to hold the phospholipids together to form membranes. carrier protein Flashcards | Quizlet Terms in this set (11) carrier protein Proteins that change shape to allow a substance to pass through the plasma membrane phagocytosis the engulfing of food by a cell facilitated diffusion Facilitated Diffusiona passive form of carrier transport exocytosis the process by which wastes are packaged in vesicles and leave the cell active transport Chapter 5: Membrane Structure and Function Flashcards | Quizlet Distinguish between channel proteins and carrier proteins. Channel proteins function by having a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or atomic ions use as a tunnel through the membrane. Carrier proteins hold on to their passengers and change shape in a way that shuttles them across the membrane. Are transport proteins specific? Building It Up and Breaking It Down: Photosynthesis vs. Cellular ...
Selective labeling of the erythrocyte hexose carrier with a maleimide ... Once reacted, the carrier was locked in a conformation unable to reorient inwardly and bind cytochalasin B. In intact erythrocytes the N-maleoylglycyl derivative of 2- ( {sup 3}H)glucosamine labeled predominantly an M {sub r} 45,000-66,000 protein on gel electrophoresis in a quantitative and cytochalasin B inhibitable fashion. PDF Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function - WOU A) Channel Proteins (e.g. Na+ channels) B) Carrier Proteins (e.g. glucose transporter) 2) Receptor Proteins: • Trigger cell activity when molecule from outside environment binds to protein 3) Recognition Proteins: • Allow cells to recognize / attach to one another • Glycoproteins: Proteins with attached carbohydrate groups Cell Respiration: Introduction - SparkNotes Cell membrane proteins (video) | Khan Academy Peripheral proteins kind of attach and remove themselves from the cell membrane or from other proteins. They generally are there for different cell processes, so for example, a hormone might be a peripheral protein, and it might attach to the cell, make the cell do something, and then leave. Peripheral proteins can also exist inside the cell on ...
cellular respiration - Students | Britannica Kids | Homework Help
H 2 O Model 3 The Electron Transport Chain Outer mitochondrial membrane ... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) HYDROGEN IONS ( H+ ) Read This! NADH and FADH 2molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported acrossthe inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
Biology A Unit 3: Lessons 11-14 Flashcards | Quizlet Carrier proteins can allow much larger substances to cross the membrane than channel proteins do. Carrier proteins undergo a shape change as they move substances across the membrane, while channel proteins do not. Channel proteins move substances across the membrane at a much faster rate than carrier proteins.
Biology A: Unit 3 Flashcards | Quizlet Channel proteins move substances across the membrane at a much faster rate than carrier proteins. Carrier proteins can allow much larger substances to cross the membrane than channel proteins do. Which type of transport does not require energy but uses carrier proteins to help move substances across the cell membrane?
PDF Model 1 Glycolysis - psd202.org Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
PDF Chapter 3 Review Materials Key - wtps.org 9. What name is given to the transmembrane proteins that allow this direct passage? 3. Figure 3.3 is a simplified diagram of the plasma membrane. Structure A repre- sents channel proteins constructing a pore, structure B represents an ATP- energized solute pump, and structure C is a transport protein that does not depend on energy from ATP.
Label-free and redox proteomic analyses of the triacylglycerol ... The expression of proteins involved in the degradation of branched-chain amino acids and the methylmalonyl-CoA pathway probably provided propionyl-CoA for the biosynthesis of odd-numbered fatty acids, which make up almost 30 % of RHA1 fatty acid composition. ... [acyl-carrier protein] synthase II (FabF). An integrative metabolic model for the ...
Carrier Protein - Definition, Function and Examples - Biology Dictionary Carrier Protein Definition Carrier proteins are proteins that carry substances from one side of a biological membrane to the other. Many carrier proteins are found in a cell 's membrane, though they may also be found in the membranes of internal organelles such as the mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleolus, and others.






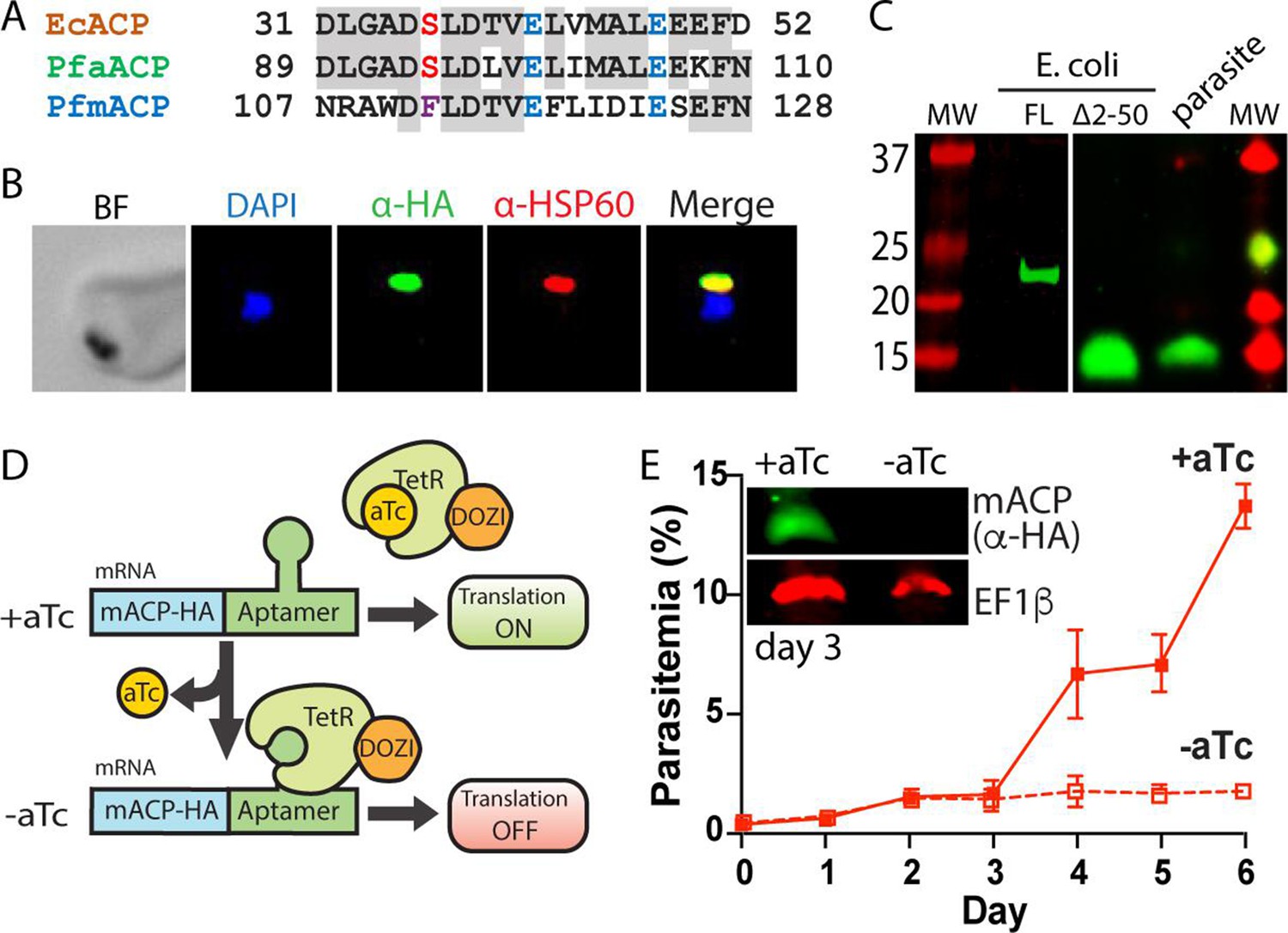

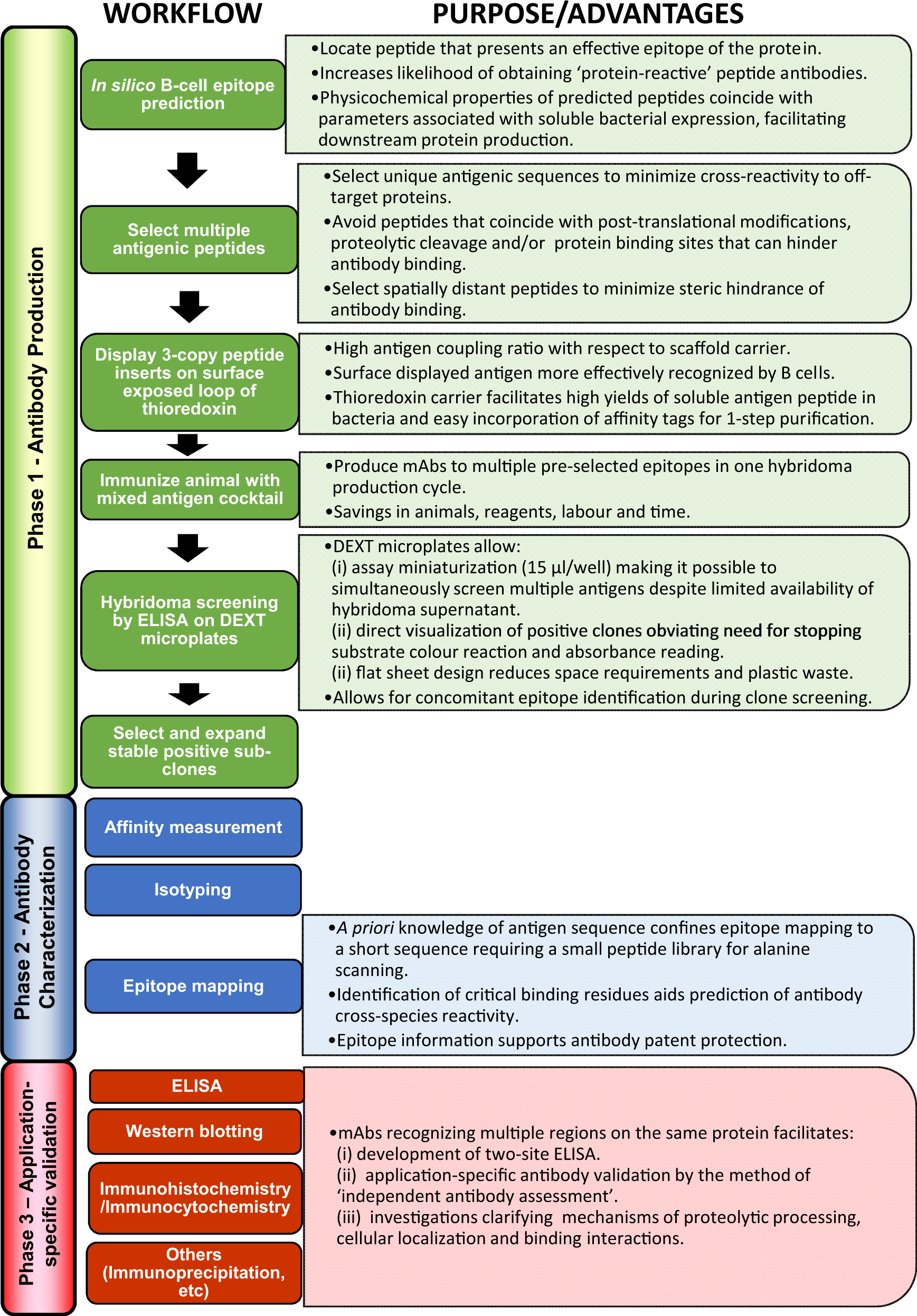













Post a Comment for "38 label the carrier proteins in model 3"